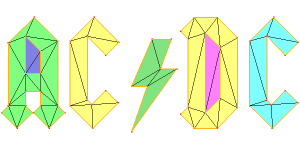
You can generate a mesh from a set of points or from a set of edges.
Mesh generation from a set of edges
We start from a mesh containing only edges (the acdcBdy.mesh file)
To generate a mesh containing this edges, we just need to run the mmg2d application. Because we don’t want to smooth the font used, we specify a sharp angle detection of 10° using the -ar option:
mmg2d_O3 -ar 10 acdcBdy.mesh
Note that mmg meshes the internal subdomains created by the edges. By default, all subdomains are saved. You can choose to keep only one subdomain using the -nsd option.
Finer mesh generation
To generate a finer mesh we can specify a maximal edge size value using the -hmax option. The mesh bounding box is of size 500×200 thus we impose a maximale edge size of 10:
mmg2d_O3 -ar 10 -hmax 10 acdcBdy.mesh
Mesh generation from a set of points
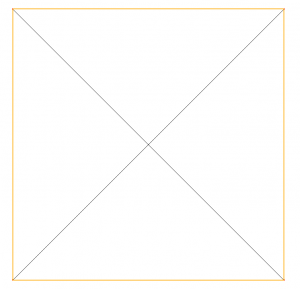
In our example, our initial mesh file (the square.mesh file) contains only points (it is represented figure 1).
To generate a mesh of the convex hull of those points, you just need to run the mmg2d application:
mmg2d_O3 square.mesh
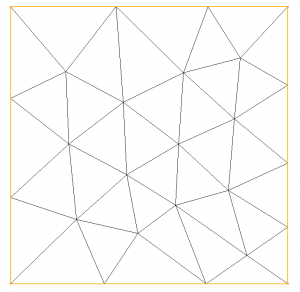
We obtain the mesh represented figure 2.
Here we have created a mesh containing all the initial vertices, then, the mesh has been optimized (as no option or size map is provided, we seek to have a high mesh quality with a minimal number of vertices).
Preservation of the initial points
You can keep your initial points using the -noinsert, -noswap and -nomove arguments:
mmg2d_O3 square.mesh -noinsert -nomove -noswap
The resulting mesh is represented figure 3.